Enterprise Data Catalog
What is Enterprise Data Catalog?
An Enterprise Data Catalog (EDC) is a tool used by organizations to help manage and organize their data assets. It provides a centralized, searchable inventory of an organization's data assets, including metadata, data lineage, data quality, and data usage information. EDCs are often used in large organizations with diverse data sources and complex data environments, where it can be difficult to track and manage data assets.
The primary purpose of an EDC is to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's data assets, which can help with data governance, data management, and data analytics. It allows users to search for and discover data assets, understand the context in which data is used, and identify relationships between data assets. EDCs can also help to identify potential data quality issues, data duplication, and data lineage, which can be useful for regulatory compliance, data security, and risk management purposes.
EDCs can integrate with other tools and systems, such as data governance tools, data quality tools, and analytics platforms, to provide a complete view of an organization's data ecosystem. They can also be used to monitor data usage and provide insights into how data is being used across an organization, which can be useful for data-driven decision-making.
EDC is a valuable tool for organizations looking to improve their data management and governance processes, as it provides a centralized view of data assets and helps to ensure that data is used in a consistent, secure, and compliant manner.
Architecture
The architecture of an Enterprise Data Catalog (EDC) typically involves a few key components that work together to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's data assets. These components include:
-
Data Collectors: EDCs use data collectors to connect to various data sources within an organization, such as databases, data warehouses, and data lakes. The data collectors extract metadata from these sources and send it to the EDC for processing.
-
Metadata Store: The metadata store is a central repository for storing and managing metadata about an organization's data assets. This metadata includes information such as data lineage, data quality, and data usage, and is used to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's data assets.
-
Search and Discovery Interface: The search and discovery interface allows users to search for and discover data assets within an organization. Users can search for data based on various criteria, such as data type, owner, or usage, and can view detailed information about each data asset.
-
Data Governance and Management Tools: EDCs can integrate with other data governance and management tools, such as data quality tools and data governance platforms, to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's data ecosystem.
-
Analytics and Reporting: EDCs can also provide analytics and reporting capabilities, which allow users to monitor data usage and identify trends and patterns in how data is being used across an organization.
Understanding the Architecture of an Enterprise Data Catalog
In today’s data-driven world, enterprises must manage vast amounts of information from various sources. To stay organized and make data accessible, many organizations use an Enterprise Data Catalog (EDC). This blog post will walk you through the architecture of an EDC system, focusing on how it ingests, processes, and catalogs data from multiple sources.
What is an Enterprise Data Catalog? An EDC is a tool that helps businesses manage their data assets by gathering metadata, offering search and discovery capabilities, tracking data lineage, and providing insight into data quality. Essentially, it serves as a centralized repository that helps users locate and understand data from diverse sources. It is especially critical for organizations that need to comply with data governance regulations or optimize their use of data across departments.
Let’s break down the architecture of an EDC, looking at how it manages data ingestion, scanning, and processing.
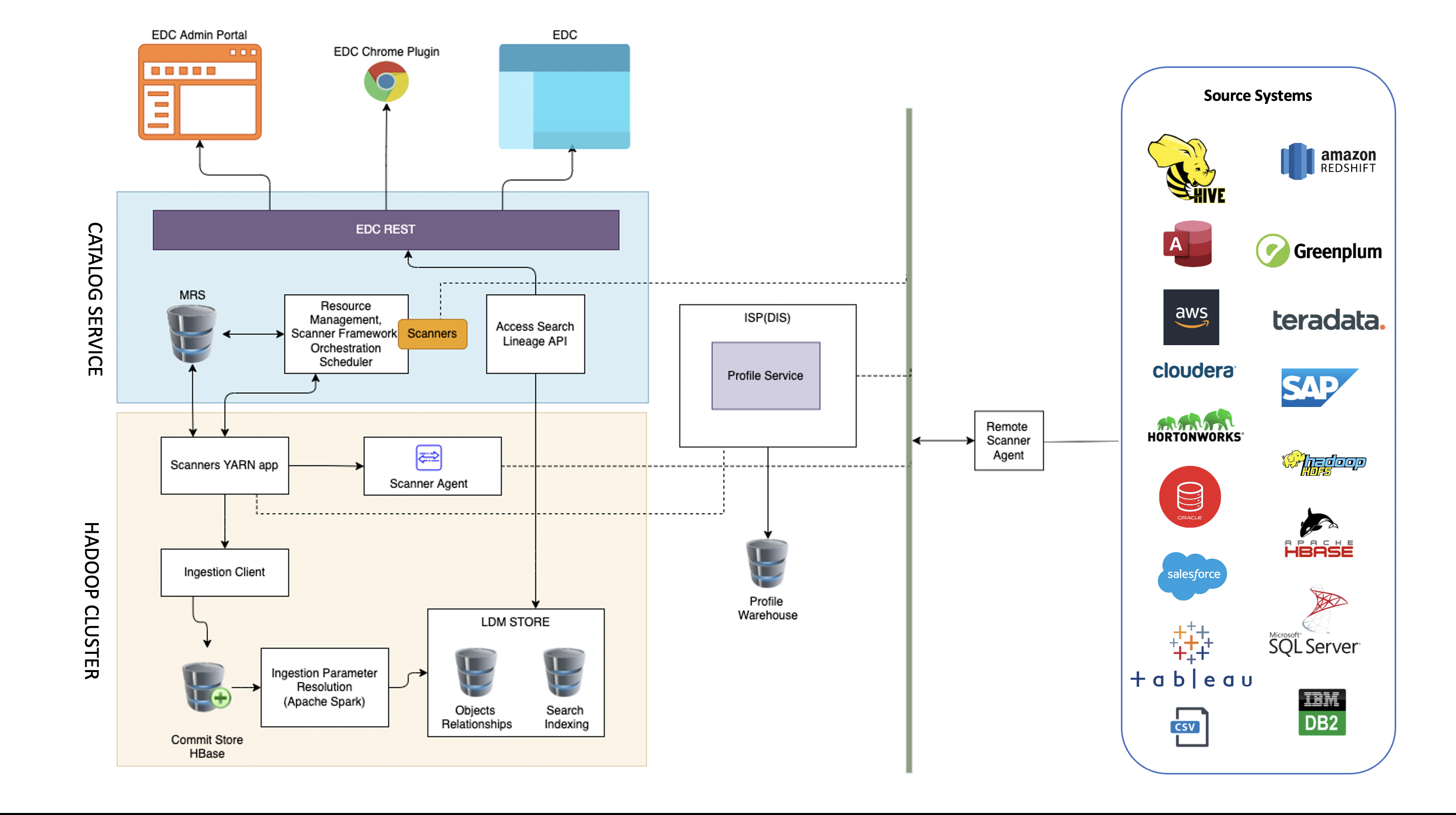
The Components of an EDC System The diagram we’re focusing on shows the Enterprise Data Catalog as a structured system divided into two main sections: the Catalog Service and the Hadoop Cluster. These components work together to create a comprehensive solution for managing data from various sources.
1. Source Systems
Data can come from many different places—cloud services, databases, applications, and file systems. In the architecture, examples of source systems include:
Amazon Redshift Hive Tableau Salesforce Microsoft SQL Server The EDC ingests data from these systems through a Remote Scanner Agent, which initiates the process of collecting metadata and organizing it into the catalog.
2. Hadoop Cluster: Ingesting and Storing Data
Once data is sourced, it flows through the Hadoop Cluster, where it is ingested and processed:
Ingestion Client: This component is responsible for gathering raw data from the source systems. Apache Spark: Spark handles the complex task of resolving ingestion parameters, preparing the data for storage. Commit Store (HBase): The processed data is stored in HBase, a distributed database, for further use. The Scanners YARN App works within this cluster, ensuring efficient resource management and orchestration. From here, the Scanner Agent manages the scanning and profiling of the data to create a structured metadata repository.
3. LDM Store: Managing Metadata
Once the data has been ingested and processed, the LDM Store (Logical Data Model Store) is used to manage important metadata such as:
Objects/Relationships: This tracks the relationships between data assets. Search Indexing: This component indexes the metadata to make it searchable for users.
4. Catalog Service: The Heart of the EDC
The Catalog Service is where users interact with the EDC, managing and accessing metadata:
EDC REST API: Provides access to data and metadata through a RESTful API, supporting data search and lineage tracking. Scanners: These scan the source systems for updates and changes, ensuring the metadata remains up-to-date. Resource Management and Scheduling: These components handle the scheduling and orchestration of scanning jobs to optimize resource usage. Metadata Repository Service (MRS): A central place to store all the metadata collected by the scanners.
5. User Interfaces: Easy Access to Data Insights
The EDC system offers multiple ways for users to interact with the catalog:
EDC Admin Portal A web-based user interface where administrators can manage the catalog and configure scanning jobs.
EDC Chrome Plugin A convenient way for users to interact with the catalog directly from their browser, allowing them to search for data, review lineage, and explore metadata.
6. Profile Service: Understanding Data Quality
A key aspect of any EDC is ensuring data quality. The Profile Service generates profiles for the ingested data, which are then stored in a Profile Warehouse. These profiles provide insights into the structure and quality of data, helping teams ensure that the data they work with meets the required standards.
Conclusion
This architecture provides a robust solution for enterprises looking to manage their data assets effectively. By breaking down the data ingestion, scanning, and cataloging processes, the system ensures that metadata is always current, accessible, and accurate. With user-friendly interfaces like the Admin Portal and Chrome Plugin, the EDC empowers teams to discover and leverage data quickly.
Ultimately, an EDC system is a vital tool for data-driven organizations, enabling them to make informed decisions, maintain compliance, and unlock the full value of their data.
This architecture demonstrates how technology can bring order to the chaos of big data—turning raw information into actionable insights, all while maintaining a high level of governance and accessibility.